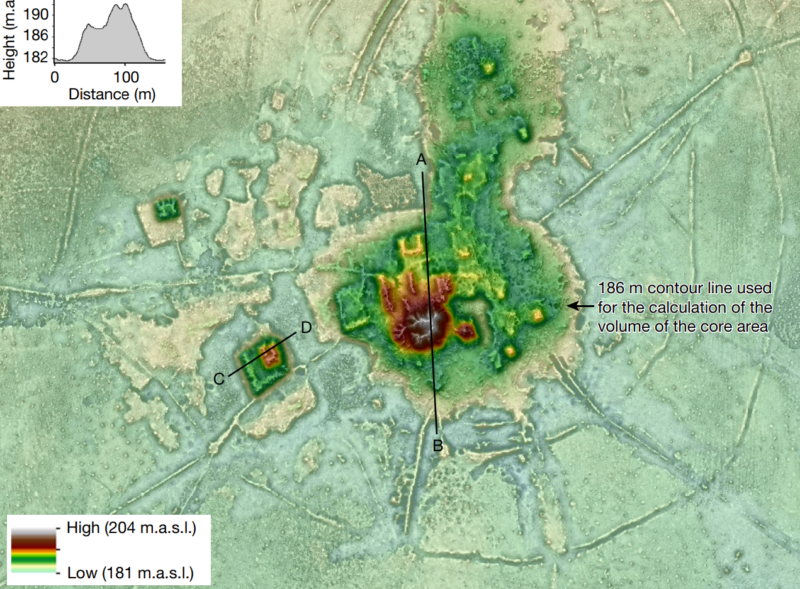
Enlarge / Cotoca, a 125 hectare settlement, sits at the center of a network of causeways linking it to smaller communities.
An airborne lidar survey recently revealed the long-hidden ruins of 11 pre-Columbian Indigenous towns in what is now northern Bolivia. The survey also revealed previously unseen details of defensive walls and complex ceremonial buildings at 17 other settlements in the area, built by a culture about which archaeologists still know very little: the Casarabe.
In the last few years, lidar—which uses infrared beams to see what lies beneath dense foliage—has helped archaeologists map a long-hidden, long-forgotten landscape of towns, fortresses, causeways, canals, terraced fields, and ceremonial sites left behind by the Maya and Olmec civilizations across a huge swath of modern Belize, Guatemala, and Mexico. Those cultures are fairly well-known to archaeologists and historians, but lidar surveys have still revealed some huge surprises. And we know far less about the Casarabe culture, as it hasn’t been the subject of as many surveys and excavations as bigger, more famous civilizations like the Maya.
But a recent lidar survey, led by Heiko Prümers of the German Archaeological Institute, shed more light (infrared, specifically) on the Casarabe culture’s network of towns and cities, linked by hundreds of kilometers of causeways and canals. The survey also revealed a thriving urban culture in an area where historians once assumed very few people lived before Spanish colonization.
Read 12 remaining paragraphs | Comments
