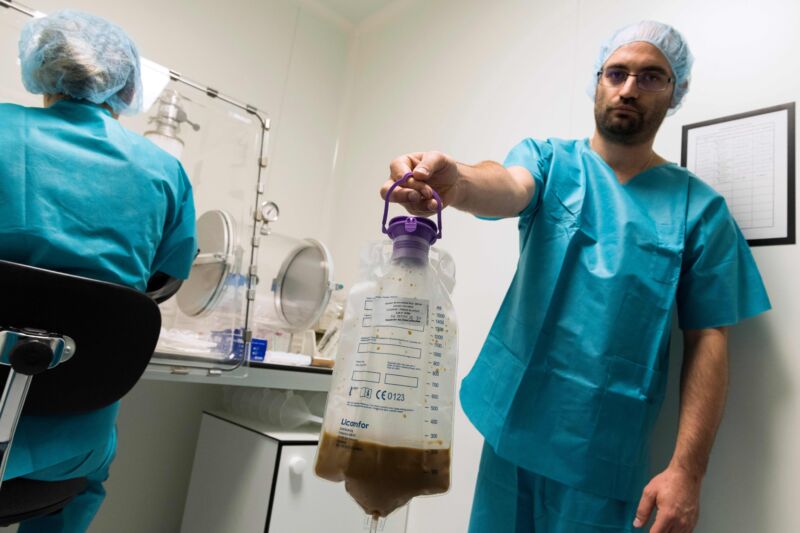
Enlarge / Laboratory technicians in France prepare stool to treat patients with serious colon infections by fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT), also known as gut flora transplant (GFT) in 2019. (credit: Getty | THIERRY ZOCCOLAN )
For the first time, the US Food and Drug Administration has granted approval for a feces-based microbial treatment, which is used to prevent a recurring diarrheal infection that can become life-threatening.
The approval, announced Wednesday, is years in the making. Researchers have strained to harness the protective qualities of the complex, diverse, yet variable microbial communities found in healthy people's intestines and stool. Early on, rich fecal matter proved useful for restoring balance and blocking infection in those whose microbiomes have been disturbed—a state called dysbiosis, which can occur from disease and/or use of antibiotic drugs. But, our understanding of what makes a microbiome healthy, functional, and protective remains incomplete.
Doctors, meanwhile, pushed ahead, informally trying an array of methods to transplant fecal microbiota from healthy donors to the guts of patients—via enemas, tubes through the nose, and oral poop-packed capsules. Fecal microbiota transplants (FMTs) have been used to treat various ailments, from obesity to irritable bowel syndrome, to mixed success. But it quickly became apparent that FMTs were most readily effective at preventing recurrent infection from Clostridioides difficile (C. difficile or just C. diff).
Read 7 remaining paragraphs | Comments
